How is interest charged?
Standard Variable Rate
This is a standard interest rate, which a lender will set and can go up or down in line with market rates (such as the Bank of England’s base rate).
Advantages:
You have more flexibility and can usually repay your mortgage without any early repayment charges.
Disadvantages:
Your monthly payments can go up and down and this can make budgeting difficult.
Standard variable rate mortgages are not usually the lowest interest rates lenders offer.
Discounted Rate
Some lenders offer mortgages where the initial interest rate is set at an amount below their standard variable rate for a set period of time. At the end of your discounted rate period, your lender will usually change your interest rate to their standard variable rate (SVR). It’s a good idea to review your mortgage at this stage because the lender’s SVR may not be the best deal around.
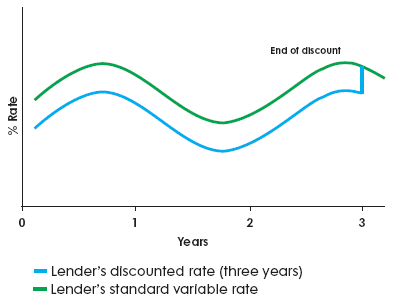
Advantages:
Your payments should cost you less in the early years, when money may be tight. But you must be confident you can afford the payments when the discount ends.
Disadvantages:
Your monthly payments can go up or down, which can make budgeting difficult.
If you want to repay the loan early, there could be early repayment charges.
Fixed Rate
With a fixed rate mortgage, your monthly payment won’t change for a set period. At the end of your fixed rate, your lender will usually change your interest rate to their standard variable rate (SVR). It’s a good idea to review your mortgage at this stage because the lender’s SVR may not be the best deal around.
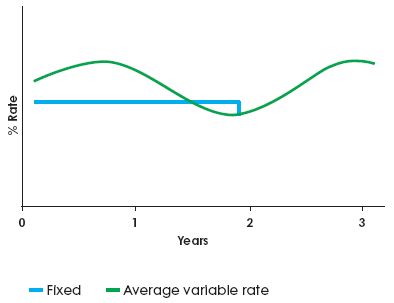
Advantages:
You know the exact amount you’ll need to pay each month, which makes budgeting easier.
Your monthly payment will stay the same during the fixed period, even if other interest rates increase.
Disadvantages:
Your monthly payment will stay the same during the fixed period, even if other interest rates decrease.
If you want to repay your loan early, there could be early repayment charges.
Tracker Mortgage
With a tracker mortgage, the interest rate charged by your lender is linked to a rate such as the Bank of England base rate. This means your payments can go up or down.
Advantages:
The rate you pay tracks another headline rate (for example, the Bank of England base rate). If the headline rate changes, your tracker rate changes by the same amount. So normally your interest rate will be following trends in the marketplace.
Disadvantages:
Some lenders impose a collar which means the interest rate won’t fall below a certain level, even if the rate it’s tracking continues to reduce.
Your monthly payments can go up or down which can make budgeting difficult.
If you want to repay the loan early, there could be early repayment charges.
Offset Mortgage
An offset mortgage is generally linked to a main current account and/or savings account, which are all held with the same lender. Each month the amount you owe on your mortgage is reduced by the amount in these accounts before working out the interest due on the loan. This means as your current account and saving balances go up, you pay less mortgage interest. As they go down, you pay more. Linked accounts that are used to reduce the mortgage interest payments do not attract interest.
Advantages:
Mortgage payments can be reduced as the level of savings increase, or you may be able to continue paying a higher level and pay your mortgage off early.
You usually pay tax on your savings. However, if your savings are automatically used to offset your mortgage, you won’t pay income tax on these savings – this is particularly beneficial for higher rate taxpayers.
Disadvantages:
All accounts have to be with one lender/bank.
You need to have a substantial level of savings.
Capped Rate or Capped and Collared Rate
With this type of mortgage, the interest rate is linked to your lender’s standard variable rate but with a guarantee that it won’t go above a set level (called the ‘cap’) for a set period, but equally won’t go below a set level (called the ‘collar’) for an agreed period of time. It’s possible to have a capped rate without a collar.
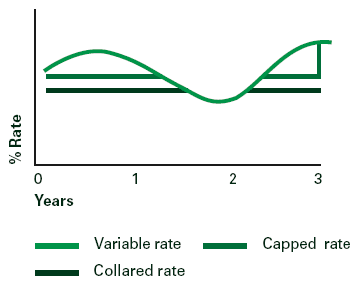
Advantages:
You know the maximum and minimum you’ll pay for a set period of time making budgeting easier.
These products are useful if you want the security of knowing that your payments can’t rise above the set level (the cap), but could still benefit if rates fall during the set period.
Disadvantages:
Even if other rates fall, your interest rate for the set period will not go down below the level of the ‘collar’.
If you want to repay the loan early, there could be early repayment charges.

